The joints of the fingers most often begin to hurt after 40-45 years (in 1 in 10 people this is due to age-related changes in the body). After 60 years, the pain often occurs against the background of polyosteoarthritis (lesions, destruction of articular cartilage in various joints).
Deformity and destruction of the joints of the hands is diagnosed in 10% of the elderly.
Also, pain in the joints of the fingers is a characteristic symptom of diseases such as:
- rheumatoid arthritis (in 80% of cases it begins with inflammation of the finger joints);
- psoriatic arthritis (70% of the fingers are the first to suffer);
- gout (arthritis affecting the fingers, occurs in 10-15% of patients with gout);
- osteomyelitis is an infectious inflammation of the bones (represents 6, 5% of all diseases of the musculoskeletal system).
Most of the arthritis in which the finger joints are first involved in the process are systemic diseases (ie they affect different systems of the body, not just the joints).They are equally often diagnosed in people of all ages, including young people, in men they are 3-5 times less common.
Another cause of pain is mechanical injury, the consequences of blows or bruises on the hands (not uncommon in athletes, the prevalence is up to 40% of all traumatic injuries).
Some of the diseases that cause pain in the joints of the fingers cannot be completely cured, over time they become a cause of disability (rheumatoid, psoriatic arthritis, polyosteoarthritis). And for example, you can get rid of osteomyelitis with timely treatment forever, but the process quickly becomes chronic and can lead to limb loss (in 30% of cases).
If you suspect a systemic disease (arthritis, polyosteoarthritis), you should consult a rheumatologist or arthrologist. Osteomyelitis is treated by an orthopedist traumatologist, surgeon, injuries - orthopedist traumatologist.
Why do finger joints cause pain: causes and symptoms
Why do finger joints hurt? There are many reasons as well as factors that can speed up or push the process. Common predisposing factors for all diseases and injuries can be considered:
- Profession (this category includes people who have to work with brushes and fingers, musicians, seamstresses, programmers).
- Loads (injuries and microtraumas as a result of hours of sports training, rehearsals).
- Hormonal changes, disorders (pregnancy, lack of estrogen in older women).
- Heredity (close relatives are more susceptible to systemic diseases).
- Deficiencies or diseases of the immune system.
- Metabolic disorders (gout, diabetes).
- Chronic infections (tuberculosis).
- Hypothermia (hypothermia).
- Some long-term negative factors (among them - medication, poisoning with toxic substances in a dangerous enterprise, smoking, alcoholism, etc. ).
The pathologies and conditions that cause pain in the joints of the fingers are described below in the article.
Trauma
The pain that comes after an injury is hard to confuse with anything else:
- all symptoms appear immediately after a blow, bruise, compression and other injuries;
- swelling, bruising at the site of impact, impaired mobility of the joints join the sharp pain;
- in moderate and severe damage the symptoms do not disappear for a long time, but become more pronounced - pain, stiffness, swelling;
- the discomfort increases when trying to bend or straighten the fingers.
Severe injuries to the fingers of the upper limb are combined with:
- ruptures of muscles, ligaments, blood vessels, hemorrhage in the capsule (hemarthrosis) and soft tissues (hematoma);
- bone fractures and cracks;
- nerve damage (loss of sensitivity in the fingers and skin).
Prognosis: minor injuries heal without a trace in 90-95% of cases. Severe and moderate injuries can leave behind various complications - from impaired sensitivity of the fingers to traumatic arthritis in 70%.
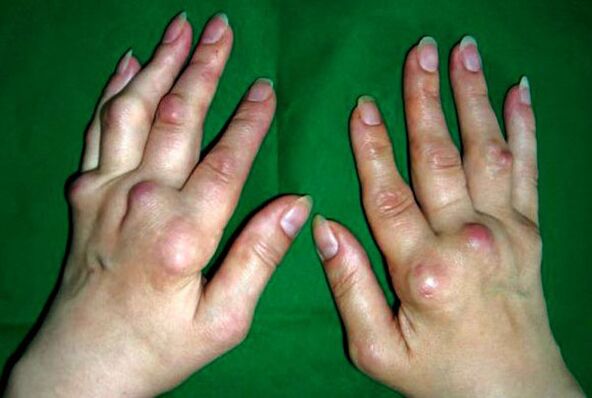
Polyosteoarthritis
Polyosteoarthritis is a chronic pathology, as a result of which the joints of the fingers are gradually deformed and destroyed (there is a form of the disease that affects the joints of the thumbs - rhizarthrosis).
Initially, the pain appears after hard work (sewing, embroidery, many hours of rehearsals on a musical instrument). As the disease progresses:
- the pain in the joints of the fingers becomes constant, does not disappear at rest;
- clicks and crunches (during movements) are accompanied by painful sensations;
- stiffness appears (initially insignificant).
During periods of exacerbation, the main symptoms are accompanied by swelling, swelling, fever and sometimes redness in the joints.
Over time, the fingers deform:
- Heberden's nodules (bone growths, pea-sized seals) form on the joints closer to the nails.
- Bouchard's nodules (proliferation of joint surfaces, bone spikes) form on the middle joints.
The joints of the fingers lose their original shape (become nodular) and over time lose their mobility due to ossification of the soft tissues (ankylosis).
Prognosis: the pathology is incurable, but in the early stages (until the appearance of the deformity) it can be stopped for a long time. Later it causes damage (tissues grow together, ossify, the mobility of the fingers can be restored only by surgery).
Rheumatoid arthritis
Chronic inflammatory disease of the joints, which occurs with the participation of other organs and systems in the pathological process (outer shell of the heart, lungs, vascular walls, skin).
Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by:
- gradual increase and increase of symptoms (in the beginning the exacerbation is replaced by quite long periods of asymptomatic course, but over time they become shorter);
- morning stiffness, reminiscent of tight gloves (disappears in 30-60 minutes);
- sharp, sharp, dull pain in the joints of the fingers (on both hands), which when folded increases to unbearable;
- redness, swelling, swelling, stiffness of the joints.
The pain syndrome usually appears at night or in the morning and decreases slightly by the afternoon.
When the acute symptoms subside (during remission), the pain becomes less pronounced, painful, increases with movement, when working in cold water. The joints of the fingers hurt when folded and unfolded, remain painful to the touch and slightly swollen.
Gradually the disease leads to the formation of stable deformation and dysfunction of the fingers - they turn outwards or upwards, bend (more often affect the middle, index and ring fingers, very rarely - the little finger and big toes), other joints are involved in the process (wrists). , ankles, knees, shoulders). . .
Prognosis: the pathology is incurable, progresses rapidly and leads to disability, to disability - 40% of cases in the first 5 years of development.
Psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a form of severe systemic disease (psoriasis).
The most characteristic signs of damage to the joints of the fingers:
- sudden, abrupt onset of arthritis;
- lesions of the interphalangeal and distal (closer to the nail) joints;
- constant, even, severe pain, combined with extensive swelling, redness of the skin, limited mobility (the shape of the fingers at this time resembles a turnip or sausage, it is impossible to bend or unfold the finger joints due to pain and swelling);
- increase in total temperature.
In the long run, this leads to destruction of the nail plates (they collapse, lose their shape), deformation of the fingers (they are "twisted" outwards or upwards) and disability.
Prognosis: Psoriatic arthritis is incurable, difficult, progresses rapidly and leads to disability in 90-95% of patients.
Gouty arthritis
Gout arthritis occurs against the background of metabolic disorders, due to which excess uric acid accumulates in the body. It enters the joint tissue, causing inflammation.
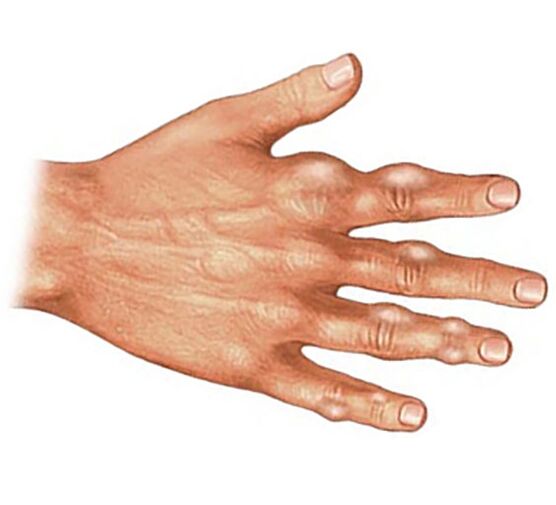
Typical signs of gouty arthritis:
- Acute, sudden, throbbing or burning pain in one or more joints of the fingers.
- Any attempt to move your finger or touch it worsens the unpleasant symptom.
- It is accompanied by severe swelling, which often spreads throughout the hand, a change in skin color (the finger becomes bluish-purple), an increase in total temperature (the patient has a fever, chills).
- Pain in the joints of the fingers usually occurs at night.
- The attack can last from 2 days to 2 weeks.
Progressive gouty arthritis causes the inclusion of new joints in the process, their deformation (destruction of joint surfaces). Tofus, tissue deposits of uric acid, appear on the fingers.
Prognosis: Gout is incurable, but uric acid levels can be maintained with medication and diet. The disease rarely causes complete damage to the patient (5-8%), but over time it can destroy the finger joints (secondary osteoarthritis).
Why else can finger joints hurt?
Other causes of pain include the following diseases and conditions:
Osteomyelitis
This infectious bone damage (periosteum, spongy and compact substance) usually begins acutely - joint pain in osteomyelitis is strong, sharp, twitching, cracking or tearing. When bending or stretching increases to unbearable, accompanied by severe swelling, redness and thickening of the tissues above the joint, fever and signs of general intoxication (weakness, sweating). In 30% of cases, osteomyelitis becomes chronic (may recur) and the pain in the fingers becomes painful. The process can cause purulent arthritis, malignant bone disease, deformity of bones and joints.
Vasospasm
Vasospasm is a sharp narrowing of the peripheral vessels that supply blood to the upper limbs, hands and joints of the fingers. It is characterized by tingling, numbness, pale skin. At the end of the attack (which can be short - from 2 minutes, or long - up to 60 minutes) the fingers begin to hurt, "hurt", and the skin of the hands becomes red. Over time, such a phenomenon (vasospasm) causes the appearance of trophic ulcers (tissue necrosis due to malnutrition), melting of the bones and necrosis of the fingertips.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is not a pathological condition, but is accompanied by abrupt and rapid hormonal changes in the body, accelerated metabolism. Pain in the joints of the fingers, or rather pain, can provoke a lack of calcium and vitamin D3, as well as an excess of the hormone that prepares the body for childbirth by loosening the ligaments.
Diagnosis: methods, research
When the toe joint hurts, what should be done? First of all, it is necessary to diagnose the pathologies that cause such a symptom. Most often, the attending physician prescribes a number of tests:
| Method name | What allows you to diagnose |
|---|---|
X-rays |
With its help pathological changes in the bones, deformation of the joints, deposition of crystals, ossification of the tissues are detected. |
MRI, CT or ultrasound |
These diagnostic methods allow you to detect any pathological changes in the periarticular tissues and joints that are not visible on X-rays. |
ECG, ultrasound of internal organs |
Helps to identify extra-articular manifestations characteristic of some diseases (pericarditis, pneumonitis) |
Angiography |
Examination of blood vessels is informative for pathologies that occur with damage to their walls and can cause vasospasm (rheumatoid arthritis) |
Clinical laboratory tests |
With the help of analyzes the cause of the disease is determined, infections and pathogens of the pathological process are detected |
Therapeutic and diagnostic puncture of the joints (procedure for extracting fluid from the joint capsule) |
A puncture is performed if blood (haemarthrosis), pus (infectious processes) or a large amount of fluid has accumulated in it, which hinders mobility and threatens to destroy it. |
Treatment: principles, drugs, features
Some of the diseases or conditions that cause pain in the joints of the fingers cannot be cured (vasospasm, osteoarthritis, psoriatic, gouty arthritis). Some are completely cured and without consequences (with timely treatment - osteomyelitis, minor and moderate injuries).
General principles of treatment, methods of pain relief
Common in the treatment of all diseases that cause pain in the joints of the fingers, is the appointment of drugs that help get rid of severe symptoms.
Usually this:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which successfully relieve inflammation and pain;
- glucocorticoids, which are prescribed if NSAIDs are ineffective;
- painkillers if joint pain cannot be relieved by other means.
As soon as the symptoms subside, the patient is prescribed: chondroprotectors to slow or prevent the destruction of cartilage and physiotherapy.
Physiotherapy stimulates metabolic processes, accelerates tissue regeneration. The most popular of the physiotherapeutic procedures for joint diseases are:
- drug electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- UHF (ultra high frequency therapy);
- reflexology (acupuncture);
- massage;
- mud therapy;
- balneotherapy (hydrotherapy);
- heating procedures (paraffin, ozokerite);
- therapeutic gymnastics (exercises to strengthen the joints of the fingers).
If it is necessary to eliminate the pain in the joints of the fingers and the reasons for them, treatment in a sanatorium can give a good result. According to the instructions of the attending physician, the patient is given the opportunity to change the climate 1 or 2 times a year, to undergo a course of restorative physiotherapy procedures, to drink mineral water from natural sources.
Characteristics of the treatment of specific pathologies
In addition to the general methods and means, there are nuances in the treatment of any pathology:
| pathology | Characteristics of treatment |
|---|---|
Trauma |
The treatment of the trauma is gradual. First, the victim received first aid (fixative bandage, ice pack for 24 hours). If necessary, a puncture is made, the integrity of the tissues is restored (in case of serious damage) and it is immobilized with plaster. On the 3-5th day, they begin to warm up, stimulating healing. |
Polyosteoarthritis |
At the beginning of the disease is effective use of chondroprotectors and physiotherapy exercises. Later, only surgery helps (the problem is solved with prosthetics). |
Rheumatoid arthritis |
Prescribe basic anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, antibacterial, anti-allergic drugs, drugs that affect the activity of the immune system. |
Psoriatic arthritis |
|
Gouty arthritis |
They treat the underlying disease (gout) by prescribing agents that regulate the formation and accelerate the excretion of uric acid, drugs that dissolve tissue salt deposits. An obligatory part of the treatment is a strict diet during an attack (table number 6), less strict diet throughout life. |
Osteomyelitis |
Surgical washing of purulent cavities in the bone tissue, opening of abscesses is performed. Antibiotics and antibacterial drugs are used for treatment. |
Vasospasm |
How to treat vasospasm? In pathology, vasodilating drugs and antispasmodics (relaxing the muscles of the vascular walls), blood thinners are prescribed. Eliminate provoking factors (eg smoking) or treat the underlying disease against which vasospasm occurs (eg rheumatoid arthritis). |
Folk remedies (treatment of pathologies, pain relief)
Pain in the joints of the fingers can also be treated with folk remedies:
- Infusion on eucalyptus leaves. Take 40 g of eucalyptus leaves, pour a liter of boiling water, leave for 60 minutes under the lid. When ready, strain, drain in a dark glass container, store in refrigerator. Take daily for 2 weeks - 3 times 50 ml, 30 minutes before meals.
- Treatment of pain in the joints of the fingers with an infusion of blackcurrant leaves. Pour 10 g of raw materials with 0, 5 liters of boiling water, boil under the lid for 20 minutes. Drink one glass 2 to 3 times a day. The duration of the course is 2-3 months.
- Warming ointment for arthritis. Take 50 g of camphor and mustard powder, dilute them in turn in 100 ml of alcohol, add egg white, whipped to a froth. Rub into brushes overnight. The treatment of the finger joints lasts 21 days, after some time the course can be repeated.
- Rubbing with oil. Dilute fir essential oil with vegetable oil (1: 1), rub into finger joints until completely absorbed at bedtime. First, they need to "warm up": boil the washed potato peel in water when the broth cools down (to keep it pleasantly warm), dip the brushes in it and hold for 15-25 minutes, then rinse them with clean water. They continue to be treated in this way for 3 weeks or until the symptoms of the disease disappear.
Prevention
How to prevent pathologies that cause pain in the joints of the fingers? For this you need:
- get rid of bad habits (quit smoking and alcohol);
- introduce into the diet foods that are good for joints and cartilage (with sufficient content of calcium, phosphorus, other minerals and vitamins, proteins);
- to undergo regular examinations, to get rid of foci of chronic infection (eg tonsillitis);
- do not overload (alternate the load with rest) and do not overcool your hands.
It is very important to strengthen the immune system (swimming, yoga, walking) and the joints of the fingers with exercises from therapeutic gymnastics.





































